The above image shows high temperature anomalies over the Arctic on June 3, 2023.
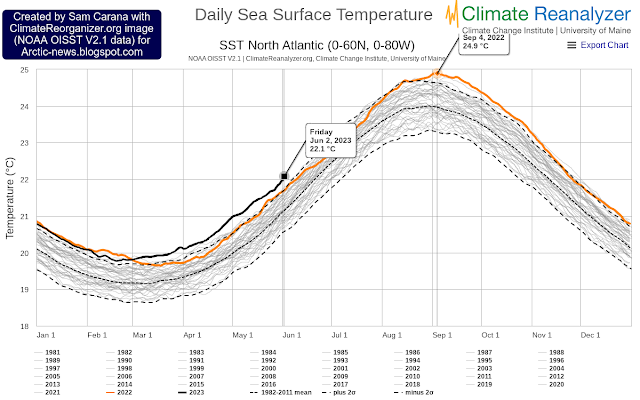
The above image shows that the sea surface temperatures on the North Atlantic (SST NA 0-60N, 0-80W) was 21.9°C on June 2, 2023 (black line), much higher than the SST on June 3, 2022 (orange).
SST NA reached a record high of 24.9°C in early September 2022, and this high temperature occurred while La Niña suppressed the temperature. This time, El Niño is on the way.
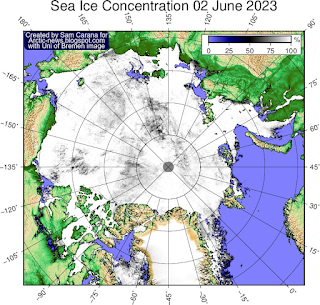
Sea ice concentration is getting lower in many places and there is open water in parts of the Beaufort Sea and Baffin Bay, as illustrated by the Uni of Bremen image on the right.
Rising temperatures in the Arctic threaten to trigger massive loss of Arctic sea ice within months. The annual Arctic sea ice extent minimum is typically reached in September and SST NA are critical in regard to melting of the Arctic sea ice.
The next image on the right, also from the Uni of Bremen, shows Arctic sea ice thickness.
 |
| [ click on images to enlarge ] |
As discussed in earlier posts such as this one, conditions are dire:
• Earth's energy imbalance is at record high
• emissions are at record high
• greenhouse gas concentrations are at record high
• temperatures are very high, especially in the Arctic
• emissions are at record high
• greenhouse gas concentrations are at record high
• temperatures are very high, especially in the Arctic
• sea ice is very vulnerable
• the Jet Stream is strongly deformed
• the Jet Stream is strongly deformed
Furthermore, El Niño is on the way, sunspots are higher than predicted and the Tonga submarine volcano did add large amounts of water vapor high into the atmosphere.
All this looks set to jointly result in massive loss of Arctic sea ice over the coming months, with loss of the latent heat buffer and loss of albedo threatening to trigger eruption of methane from the seafloor of the Arctic Ocean, as has been described many times before, such as in this post, in this post and in this post.
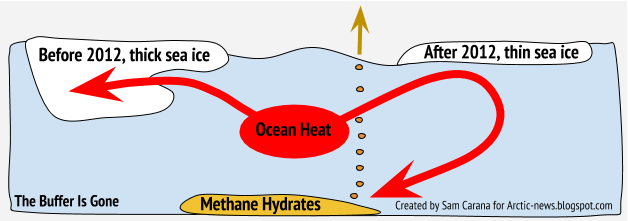 |
| Latent heat loss, feedback #14 on the Feedbacks page |
 |
| [ see the Extinction page ] |
The bar on the right depicts the threat, as further discussed at the Extinction page.
In conclusion,
Links
https://climatereanalyzer.org/wx/todays-weather/?var_id=t2anom&ortho=1&wt=1
• Climate Reanalyzer - Daily sea surface temperatures
https://climatereanalyzer.org/clim/sst_daily
• University of Bremen - sea ice concentration and thickness
https://seaice.uni-bremen.de/start
• Polar Portal - Arctic sea ice thickness and volume
http://polarportal.dk/en/sea-ice-and-icebergs/sea-ice-thickness-and-volume
• Wetland emission and atmospheric sink changes explain methane growth in 2020 - by Sushi Peng et al.
https://www.nature.com/articles/s41586-022-05447-w
• Will there be Arctic sea ice left in September 2023?
• Will there be Arctic sea ice left in September 2023?
• Climate Plan
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climateplan.html
• Climate Emergency Declaration
https://arctic-news.blogspot.com/p/climate-emergency-declaration.html

 11 months ago
62
11 months ago
62